Table of Contents
Blue Economy and its Components | UPSC – IAS
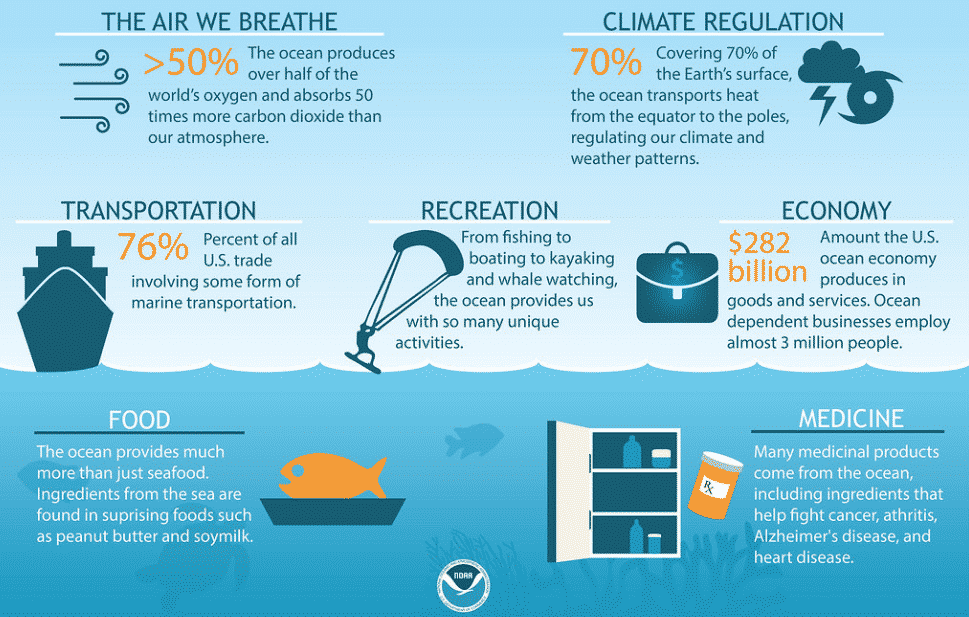
As per the World Bank, Blue Economy is the sustainable use of ocean resources for economic growth, improved livelihoods, and jobs while preserving the health of ocean ecosystem. It covers several sectors linked directly or indirectly to the oceans such as –
- Fishing, minerals, shipping and port infrastructure,
- Marine biotechnology,
- Marine renewable energy,
- Marine tourism,
- Ocean governance and education.
Significance of Blue economy | UPSC – IAS
Economic Benefits:
- Oceans provide 30 percent of oil and gas resources.
- 90% of goods trade takes place through Oceans Sea of Line Communication.
- Ocean contributes $2.5 trillion to world economy with around 60 million people are employed in fisheries and aquaculture.
- Seabed Mining of polymetallic nodules and polymetallic sulphides to extract nickel, cobalt, manganese and rare earth metals.
Environmental Benefits:
- Mangroves and other vegetated ocean habitats sequester 25 percent of the extra CO2 from fossil fuels, i.e., Blue Carbon.
- Protection of coastal communities from disasters like floods and storms.
- A Sustainable Blue Economy can help to achieve commitments under UN’s Sustainable Development Goals 2030, Paris climate agreement 2015 and the UN Ocean Conference 2017.
Challenges to Blue Economy | UPSC – IAS
- Unsustainable development near marine areas: Physical alterations and destruction of marine and coastal habitats & landscapes largely due to coastal development, deforestation, & mining.
- FAO estimates that approximately 57 percent of fish stocks are fully exploited and another 30 percent are over-exploited, depleted, or recovering.
- Marine pollution: It is in the form of excess nutrients from untreated sewerage, agricultural
runoff, and marine debris such as plastics. Deep sea mining can cause long term irreversible ecological damage to marine ecosystem. - Impacts of climate change: Threats of both slow-onset events like sea-level rise and more intense and frequent weather events like cyclones. Long-term climate change impacts on ocean systems like changes in sea temperature, acidity, and major oceanic currents.
- Geopolitical issues: Geopolitical tussle between in various regions like South China Sea, Indian Ocean Region etc. and undermining International Laws like UNCLOS limits the countries from achieving the full potential of Blue Economy.
- Unfair trade practices: Many times fishing agreements allow access to an EEZ of country to foreign operators. These operators restrict transfer of specific fishing knowledge to national stakeholders leading to low appropriation of fisheries export revenues by national operators. So the potential for national exploitation of those resources is reduced in the long run.
- Other non-conventional threats: Defense and security related threats like piracy and terrorism combined with natural disasters (Small Island Developing States are particularly vulnerable).
Blue economy and India | UPSC – IAS
India is trying to achieve the potential of Blue Economy by promoting the spirit of ‘SAGAR-Security and Growth for All in the Region’ in Indian Ocean Region. Some initiatives by India are: (important for UPSC)
Sagarmala Project: Sagarmala initiative focus on three pillars of development
- Supporting and enabling Port-led Development through appropriate policy and institutional interventions.
- Port Infrastructure Enhancement, including modernization and setting up of new ports.
- Efficient Evacuation to and from hinterland by developing new lines/linkages for transport (including roads, rail, inland waterways and coastal routes).
- Coastal Economic Zones: 14 CEZs are being developed under Sagarmala initiative covering all the Maritime States.
- CEZs are spatial economic regions comprising of a group of coastal districts or districts with a strong linkage to the ports in that region.
- CEZ will help to tap synergies of planned economic corridors.
- Resource exploration: India in recent times has shifted its focus towards Indian Ocean resource exploration. E.g. India has explored 75000 sq km of Indian Ocean Seabed and is developing technologies (like remotely operated vehicles) for mining the resources
- International relations and security: India is cooperating with Indian Ocean littoral countries and projecting itself as ‘net security provider’ to ensure a safe, secure and stable Indian Ocean Region (IOR). India is also cooperating with extra regional powers like US, Japan in IOR. E.g. Asia-Africa growth corridor, QUAD etc.
Sustainable Blue Economy Conference
- It’s the first global conference on the sustainable blue economy.
- It was convened by Kenya and co-hosted Canada and Japan.