Table of Contents
Recently a new study by World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) found that under optimal conditions, tiger numbers can triple in 18 sites across the world, including eight in India.
- Another study by researchers has found Royal Bengal Tiger in the snow-capped regions of the Eastern Himalaya at an altitude of more than 4,000m in Dibang valley of Arunachal Pradesh.
More on News - This new assessment could guide planning for tiger recovery globally and help inform more effective, integrated approaches to tiger conservation.
- The presence of the big cats in Dibang valley which is not even a tiger reserve is a tribute to the ways the people there have been coexisting with the animals.
Threats to Tiger Population in India
Important Facts Wildlife Protection Tiger Conservation Project | UPSC – IAS | PCS | PIB
- Indian Tiger or Royal Bengal Tiger (Panthera tigris) is the sub species found in India.
- Conservation status of Tiger
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- Wild life protection Act : Schedule 1
- CITES: Appendix 1
- The tiger reserves are constituted on a core/buffer strategy. The core areas have the legal status of a national park or a sanctuary. The buffer or peripheral areas are a mix of forest and non-forest land, managed as a multiple use area.
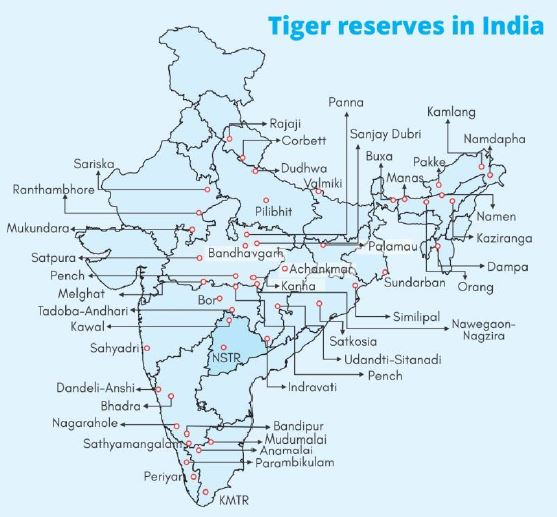
- India is home to 70 per cent of global tiger population.
- The tigers are an “umbrella” species as by rescuing them, we save everything beneath their ecological umbrella – everything connected to them.
- Highest number of tigers are in Karnataka followed by Uttarakhand
Habitat loss | UPSC – IAS | PCS | PIB
- Industrial Development has led to increased pressure on their natural habitat due to increased deforestation.
- Forest fires and floods leading to habitat loss also continue to pose a threat to their survival.
- National Highways often run through the tiger reserves which in turn lead to habitat fragmentation.
- Poaching: Tigers have been illegally hunted due to their demand in traditional Chinese medicines, decorative works, etc.
- Man-Animal conflict: Growing incidents of human–tiger conflict protected also pose significant challenge.
- Inbreeding of the tiger species is also a major concern as inbred animals are prone to acquiring crippling defects, lack of capacity to adapt and psychological issues.
Conservation Efforts in India | UPSC – IAS | PCS | PIB
- Project Tiger: The Government of India launched the centrally Sponsored Scheme the ‘Project Tiger’ in 1973 for for in-situ conservation of wild tigers in designated tiger reserves. The Project Tiger coverage has increased to 50 tiger reserves at present.
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA): It is a statutory body established in 2006 under MoEFCC performing functions as provided in the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972. Presently It implements major tiger conservation initiatives like project tiger, Tiger conservation plan etc.
- Monitoring System for Tigers – Intensive Protection and Ecological Status (M-STrIPES): It is a software-based monitoring system launched across Indian tiger reserves by the NTCA.
Global Conservation Efforts - The Global Tiger Initiative (GTI): It was launched in 2008 as a global alliance of governments, international organizations, civil society, the conservation and scientific communities and the private sector and includes organization like the World Bank, the Global Environment Facility (GEF), etc. It aims to work together to save wild tigers from extinction. In 2013, the scope was broadened to include Snow Leopards. The initiative is led by the 13 tiger range countries (Bangladesh, Bhutan, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Lao PDR, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nepal, Russia, Thailand, and Vietnam).
- The Global Tiger Forum (GTF) is the only inter- governmental international body established with members from willing countries to embark on a global campaign to protect the Tiger.
- TX2: In 2010, the St. Petersburg Declaration on Tiger Conservation was adopted under the GTI and the Global Tiger Recovery Programme or TX2 was endorsed. Its goal was to double the number of wild tigers across their geographical areas. The WWF is implementing the programme in 13 tiger range countries.
- Conservation Assured Tiger Standards CA|TS: It is a new tool for tiger conservation management. It is a set of criteria which allows tiger sites to check if their management will lead to successful tiger conservation. It is an important part of Tx2 programme.
Way Forward | UPSC – IAS | PCS | PIB
- Awareness: Awareness about tiger conservation through discussions, exhibitions and local campaigns, etc should be spread.
- Strengthening monitoring activities by authorities is a crucial element in tiger conservation. Improving the intelligence and information sharing mechanism is a major aspect in this regard. Drones can also be widely used for monitoring.
- Stopping Illegal trade: Items prepared from tiger killed must be tackled as it effectively fuels the poaching process.
- Involving Local communities: Peaceful coexistence with voluntarily participation of the local communities is a must. For example villagers must be instantaneously compensated for their cattle loss or crop damage due to tiger and other wildlife activities.
- Relocation of tigers: It should be done in a well-planned manner else there is a high chance of losing the animal. This can also help to prevent inbreeding of the tiger species and thus increase the viability of the tiger population.