Table of Contents
Indian Human Microbiome Initiative | UPSC – IAS | PIB
Indian Human Microbiome Initiative Project, led by The National Centre for Microbial Resource (NCMR) – National Centre for Cell Science (NCCS) has been put up for approval.
What is Microbiome? | UPSC – IAS | PIB
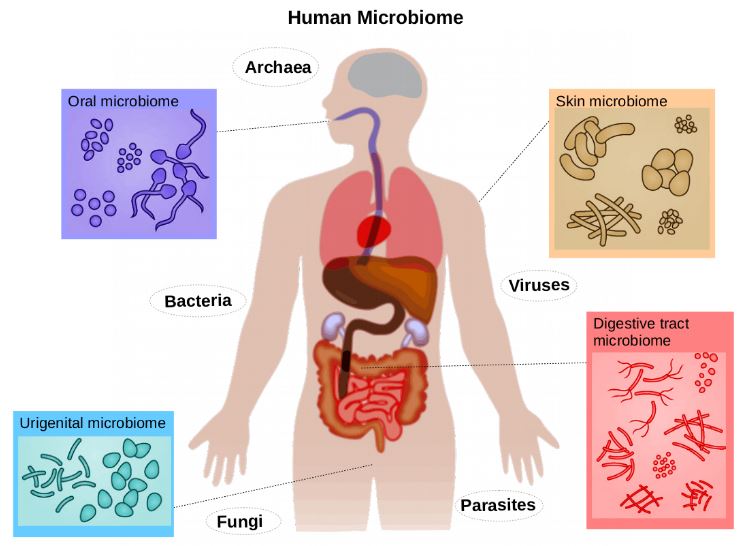
- The collective genome of all micro-organisms contained within the human body, residing inside tissues & bio-fluids is called Human Microbiome. It includes bacteria, archaea, fungi, protists and viruses.
- Most of them have either commensal (co-exist without harming humans) or mutualistic (each benefit from the other).
- Different parts of human body including the skin, mammary glands, placenta, uterus, ovarian follicles, lungs, saliva, oral mucosa, conjunctiva, biliary and gastrointestinal tracts, are occupied by characteristic microbial populations.
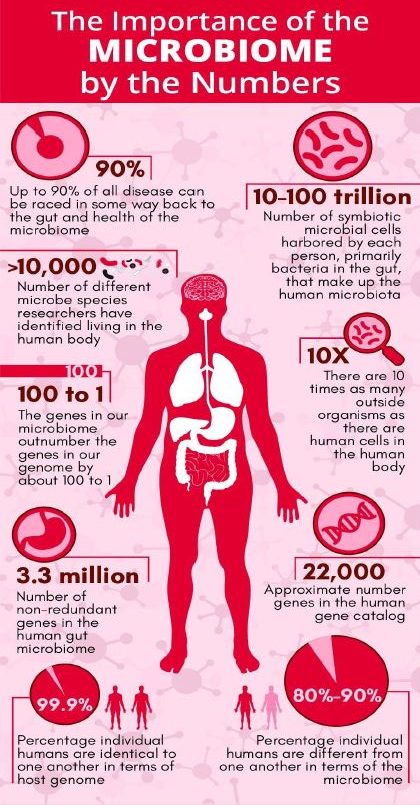
- The composition of microbiome is shaped by factors such as genetics, dietary habits, age, geographic location and ethnicity. Human microbiome makes up around 2% of the body mass of the adult.
Importance of the Human Microbiome | UPSC – IAS | PIB
Microbial communities play a key role in many aspects of host physiology:
- Metabolism of otherwise complex indigestible carbohydrates and fats
- Production of essential vitamins
- Maintaining immune systems
- Acting as a first line of defense against pathogens
- Influence the susceptibility to certain infectious diseases, as well as contribute to disorders such as obesity and diabetes
- Determines how one responds to a particular drug treatment
The diversity of microbes that make up human microbiome could lead to novel therapies e.g. an infection caused by a ‘bad’ bacterial species can be treated by promoting the growth of ‘good’ bacteria.
About Human Microbiome Project (HMP) | UPSC – IAS | PIB
- Human Microbiome Project is a research initiative of US’s National Institute of Health with the mission to generate the resources and expertise needed to characterize the human microbiome and analyze its role in health and disease.
- Launched in 2007, it is focused on identifying and characterizing human microbial fauna and elucidating their roles in health and diseases.
- Some methodologies used in HMP are:
- o Metagenomics as a culture-independent method of broad microbial community characterization
- o Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) to provide a “deep” genetic perspective on aspects of a given microbial community, i.e. individual bacterial species
Human Microbiome Research in India | UPSC – IAS | PIB
- India doesn’t have a dedicated national human microbiome project. But, the proposed Indian Human Microbiome Initiative holds a lot of potential.
- The project will include collection of saliva, stool and skin swabs of 20,000 Indians across various ethnic groups from
different geographical regions. India provides for a wide range of research with more than 4,500 ethnic groups and presence of two global biodiversity hotspots (Himalayan range and Western Ghats). - Scientists have found that Indian population, particularly tribals, have distinct gut microbiota than individuals from other parts of the world. Such tribal populations largely unaffected by “modern” diet and have lower prevalence of lifestyle diseases and their study would shed some light on mutualism between gut microbiota and the host.
Key terms Explanation
What is Metagenomics ? | UPSC – IAS | PIB
- It is a sequence-based approach that allows the genetic material from the complete collection of microbes to be analyzed in their natural environment without needing to cultivate the microorganisms.
- Currently, only a small percentage of the bacteria that comprise the human microbiome have been identified and studied. Majority (>95%) of them are difficult to isolate and culture, because the required growth conditions cannot be reproduced in the laboratory.
- However, recent technological advances in DNA sequencing and the development of meta-genomics have now made it feasible to analyze the entire human microbiome.