Table of Contents
Understanding the Earthquakes and Volcanoes | UPSC – IAS
In order to understand concept of ring of fire, it is important to first conceptualize the overarching context within which various factors operate.
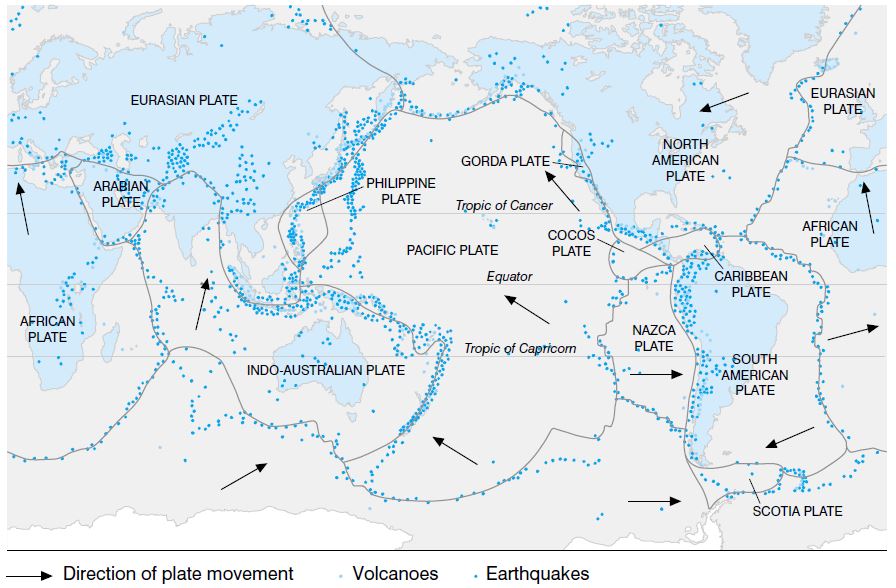
- Both earthquakes and volcanoes can be explained by the theory of plate tectonics. The earth’s crust consists of a series of plates. There are seven main plates and many smaller ones. Some plates consist of continental crust others are made of largely oceanic crust.
- Convectional activity causes the plates to move. The edges of plates are called plate margins. There are three types of plate margins. At a destructive boundary the plates move together, but at a constructive boundary the plates move apart. At a conservative boundary the plates move side by side.
- At a constructive boundary molten rock or magma rises to the surface forming new crust. This forces the existing crust apart causing sea floor spreading. This causes continental drift. At destructive margins one plate is forced under another into the subduction zone
- Volcanoes occur where there is a weakness in the earth’s crust. This allows magma to move to the surface where it forms lava. An active volcano is one that has erupted in living memory. A dormant volcano is one that last erupted in historical times. It can never be assumed that a volcano is extinct.
- Seismic waves, as a result of plate movement, cause earthquakes. The focus of an earthquake is a fault deep in the earth’s crust. The shock waves move out from the focus and reach the earth’s surface at the epicentre. Most earthquakes occur along plate margins.
Read more in Detail –
Importance of Ring of Fire and its Map| UPSC – IAS
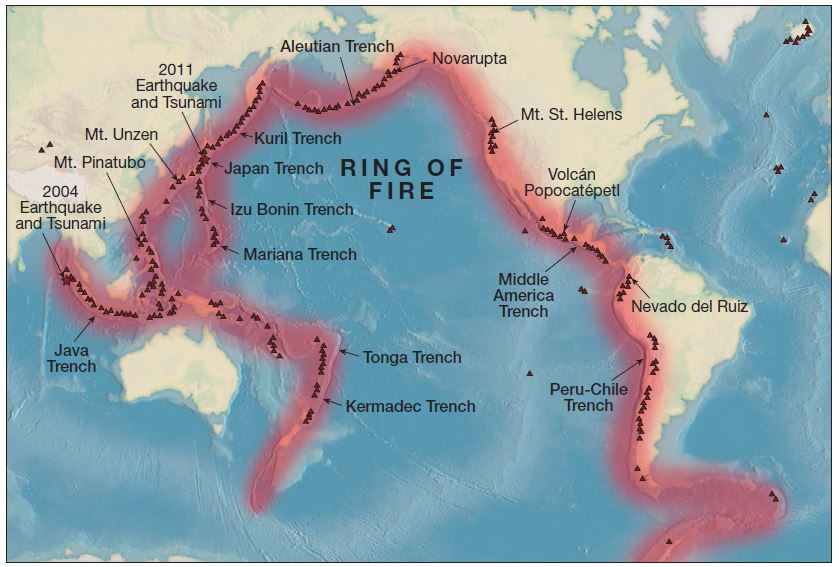
The Pacific Ring of Fire is a major area in the basin of the Pacific Ocean where many earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur. The Ring of Fire also known as the Rim of Fire or the Circum-Pacific belt. It is associated with a nearly continuous series of-:
- Oceanic trenches,
- Volcanic arcs,
- volcanic belts and
- Plate movements
Why is it called the ring of fire ?
For many decades, geologists noted the high number of earthquakes and active volcanoes occurring around the rim of the Pacific Ocean basin. About three-quarters of all active volcanoes in the world lie within the Pacific Rim, but it was only in the late 1960s that the theory of plate tectonics provided an explanation for this pattern. How many volcanoes are in the ring of fire? – It has 452 volcanoes (more than 75% of the world’s active and dormant volcanoes).
- Plate boundaries are found all of the way around the Pacific basin—primarily subduction zones, along with segments of transform and divergent boundaries.
- It is along these plate boundaries that the many volcanoes and earthquakes take place in what is now called the Pacific Ring of Fire.
- The Pacific Rim is home to millions of people. Active or potentially active volcanoes and major faults systems are within sight of some of the largest metropolitan regions in the world, such as Mexico City, Los Angeles, and Tokyo.
What are the Causes ? | UPSC – IAS
Ring of Fire is a direct result of plate tectonics: the movement and collisions of lithospheric plates. (Ring of Fire is caused by the amount of movement of tectonic plates in the area.) The massive volcanic and seismic activity that characterizes the Ring of Fire results from the activity of the tectonic plates that make up the crust.
- The eastern section of the ring is the result of the Nazca Plate and the Cocos Plate being subducted beneath the westward-moving South American Plate.
- The Cocos Plate is being subducted beneath the Caribbean Plate, in Central America. A portion of the Pacific Plate and the small Juan de Fuca Plate are being subducted beneath the North American Plate. Along the northern portion, the northwestward-moving Pacific Plate is being subducted beneath the Aleutian Islands arc.
- Farther west, the Pacific Plate is being subducted along the Kamchatka Peninsula arcs to the south past Japan. The southern portion is more complex, with a number of smaller tectonic plates in collision with the Pacific Plate from the Mariana Islands, the Philippines, Bougainville, Tonga, and New Zealand; this portion excludes Australia, since it lies in the center of its tectonic plate.
- Indonesia lies between the Ring of Fire along the northeastern islands adjacent to and including New Guinea and the Alpide belt along the south and west from Sumatra, Java, Bali, Flores, and Timor.
In recent decades we have had many reminders of the ever-active Ring of Fire volcanoes:-
- 1980 Mount St. Helens eruption;
- 1985 Nevado del Ruiz volcano tragedy in Colombia;
- 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines;
- 1994 Northridge earthquake in California;
- December 2004 Sumatra, Indonesia, earthquake and tsunami that killed more than 227,000 people; and
- March 2011 earthquake and tsunami that killed 15,000 people in Japan.
Sociological Effects of Earthquakes | UPSC – IAS
- Less Economically Developed Country suffer the greatest loss of life from earthquakes. This is because buildings are not as strong and emergency services are not as efficient. The economic cost of earthquakes can be greater in MEDCs (MEDCs are countries which have a high standard of living and a large GDP) as the economic life of a MEDC suffers greater disruption.