System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting And Research (SAFAR) | UPSC – IAS
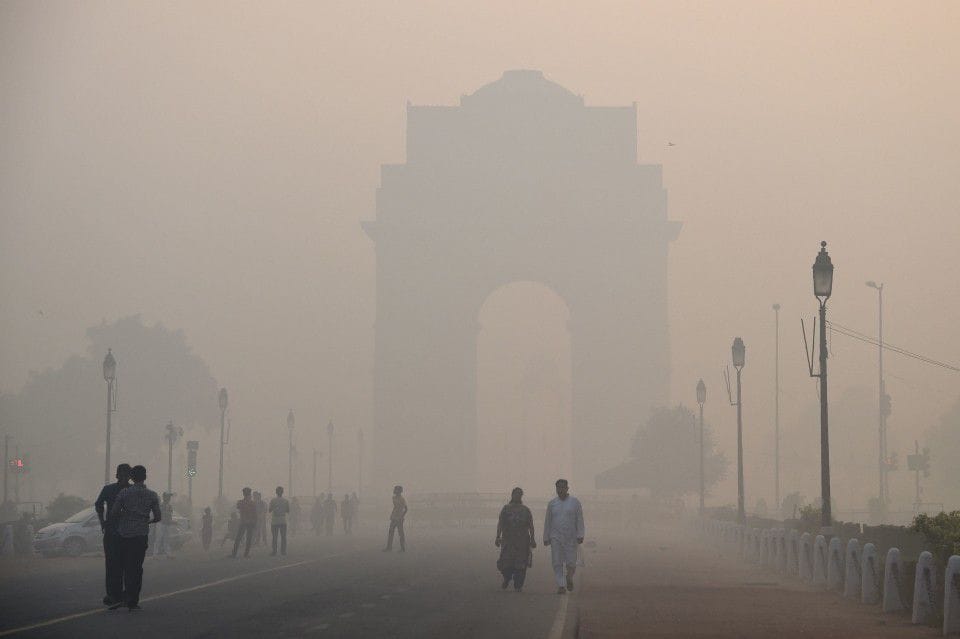
SAFAR is a national initiative introduced by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) to measure the air quality of a metropolitan city, by measuring the overall pollution level and the location-specific air quality of the city.
SAFAR envisages a research based management system where strategies of air pollution mitigation go hand in hand with nation’s economic development to target a win-win scenario.
- It is first of its kind and most advanced system in India. Such advanced are also proposed to be implemented in other three cities of India- Pune, Mumbai and Ahmedabad.
- SAFAR was developed indigenously by Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune and operationalized by India Meteorological Department (IMD).
- The ultimate goal of the project is to increase awareness among the general public regarding the air quality in their city so that appropriate mitigation measures and systematic action can be taken up.
- It organizes awareness drive by educating the public (prompting self-mitigation), and
- It also helps the policy-makers to develop mitigation strategies keeping in mind the nation’s economic development.
- SAFAR is an integral part of India’s first Air Quality Early Warning System operational in Delhi.
- It monitors all weather parameters like temperature, rainfall, humidity, wind speed, and wind direction, UV radiation, and solar radiation.
- Pollutants monitored: PM2.5, PM10, Ozone, Carbon Monoxide (CO), Nitrogen Oxides (NOx), Sulfur Dioxide (SO2), Benzene, Toluene, Xylene, and Mercury.
- SAFAR has giant true colour LED display which gives out real-time air quality index on 24×7 basis with colour coding alongwith 72-hour advance forecast.
- The World Meteorological Organization has recognized SAFAR as a prototype activity on the basis of the high-quality control and standards maintained in its implementation.
- Besides health, SAFAR system will benefit cost savings to several other sectors like agriculture, aviation, infrastructure, disaster management skill, tourism and many others, which directly or indirectly get affected by air quality and weather.