Table of Contents
Alcohol prohibition and directive principles of state policy (DPSP) | UPSC -IAS
- The directive principles of state policy (DPSP) in the constitution of India (article 47) state that “the State shall endeavor to bring about prohibition of the consumption except for medicinal purposes of intoxicating drinks and of drugs which are injurious to health”.
- The Directive Principles are not-justiciable rights of the people but fundamental in the governance of the country. It shall be the duty of the State to apply these principles in making policy laws per Article 47.
- As Per Article 38, state and union governments, as duty, shall make further detailed policies and laws for implementation considering DPSPs as fundamental policy. In contrary to Article 37, many policies have been implemented by states and union government which go against the DPSPs such as using intoxicating drinks as source of major tax revenue instead of implementing prohibition for better health of people.
- When the union government feels that alcohol prohibition is no longer useful to the nation, it shall be deleted from DPSPs by bringing a constitutional amendment to remove ambiguity in policy making / direction.
- Judiciary can repeal any policy/law devised by the government which is diametrically opposite to any DPSP. An existing policy in line with DPSP can not be reversed, however it can be expanded further in line with DPSP. The policy changes applicable under DPSP shall not be reversible unless the applicable DPSP is deleted by constitutional amendment.
- Many states imposed prohibition of alcohol and later prohibition lifted to collect more revenue/taxes by the states. Lifting / relaxing prohibition of alcohol is unconstitutional which is reversing the earlier implemented policy as per Article 37 as long as alcohol prohibition is part of DPSP.
National Prohibition was advocated by Mahatma Gandhi, as well as by many Indian women. Prohibition, in the states of India that have implemented the policy, has led to lower rates of drinking among men, as well as a decreased incidence of violence against women.
Temperance movement in India | UPSC – IAS
- The temperance movement in India aims at curbing the use of alcohol in that country. In some places, the temperance movement has led to alcohol prohibition in India, with many temperance organisations continuing their work today.
- The temperance movement in India often led to the prohibition of alcohol in various states, as with Manipur. In British India, many Indian temperance activists agitated for prohibition in the country.
- Mahatma Gandhi was a champion of the temperance movement and viewed foreign rule as an obstacle to national prohibition. When India gained independence in 1947, prohibition was included in the Directive Principles of the Constitution of India and the government of several states such as Gujarat introduced it.
What are Dry days ? | UPSC – IAS
Dry Days are specific days when the sale of alcohol is prohibited. Dry Days are fixed by the respective state government. Most Indian states observe dry days on major religious festivals/occasions depending on the popularity of the festival in that region.
- National holidays such as Republic Day (26 January),
- Independence Day (15 August) and
- Gandhi Jayanti (2 October) are usually dry days throughout India.
- National dry days also occur during Election Commission of India-ordained voting and result days.
Dry days also depend on the establishment selling alcohol. For example, generally 5-star hotels do not have to observe all the dry days that liquor stores and small bars may have to. Dry days are also observed on and around voting days.
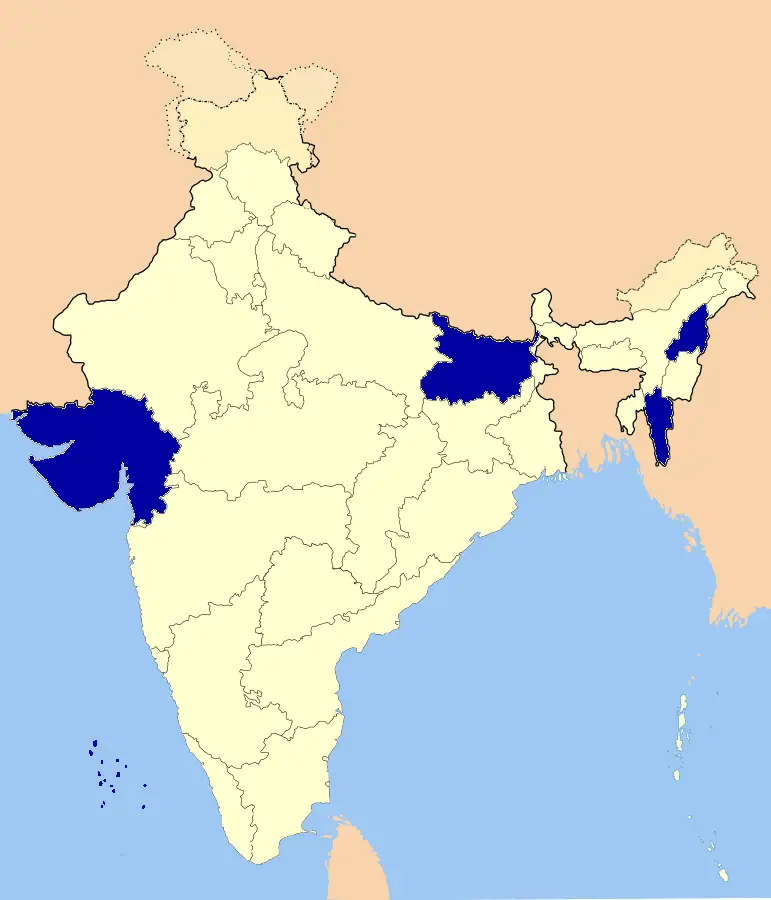
States practicing prohibition | UPSC – IAS
Alcohol prohibition in India is in force in the states of Bihar, Gujarat, Mizoram, Nagaland as well as in the union territory of Lakshadweep. All other Indian states and union territories permit the sale of alcohol.
Alcohol prohibition in Bihar | UPSC – IAS
- Bihar Chief Minister Nitish Kumar officially declared the total ban on 5 April 2016, and said in a press conference, “All type of liquor will be banned in the state from today. Sale [and consumption] of any type of alcohol in hotels, bars, clubs and any other place will be illegal from today onwards.”
Violation of law
- Violating the law carries a penalty of 5 years to 10 years imprisonment. On 30 September 2016 Patna High Court ruled that the ban is “illegal, impractical and unconstitutional”.
- Although even before the High Court order came, the Bihar government had announced that it would enforce a new stringent law from 2 October 2016, only to stay adamant on it after the order. The government had drafted a new law to keep from withdrawing the ban.
- As per the new liquor law, those found indulging in unlawful import, export, transport, manufacture, possession, sale, intoxicant or liquor could attract a minimum 10 years of jail term which may extend to imprisonment for life besides a minimum fine of Rs 1 lakh which may extend to Rs 10 lakh.
Historic Human Chain
- On 21 January 2017, more than 3 crore people of Bihar joined hands to form a historic human chain along 12,760 km of roads to support ban on alcohol by Bihar C.M Nitish Kumar. This unprecedented and massive human chain was supported by people from all walks of life and political parties.
Social and Economic effects of alcohol Prohibition in Bihar | UPSC – IAS
Prohibition, in the states of India that have implemented the policy, has led to lower rates of drinking among men, as well as a decreased incidence of violence against women. In the state of Bihar it is observed that:-
- Within a year of prohibition, the number of murders and gang robberies decreased by 20%.
- The number of riots fell by 13% and traffic accidents were reduced by 10%.
- For the economy – spending per household rose: increase in sales of milk by 10%, cheese by 200%, two-wheeled vehicles by 30%, and electrical appliances by 50%.
- In villages, brick houses are gradually taking the place of more rudimentary cottages since state Prohibition came into effect.
- At the same time, substance abuse has increased significantly due to liquor being hard to access.
Alcohol prohibition in Gujarat | UPSC – IAS
- Bombay State had prohibition between 1948 and 1950, and again from 1958. Gujarat has a sumptuary law (laws that try to regulate consumption.) in force that proscribes the manufacture, storage, sale and consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- The legislation has been in force since 1 May 1960 when Bombay State was bifurcated into the states of Maharashtra and Gujarat.
- Bombay Prohibition Act, 1949 is still in force in Gujarat state, however there is licensing regime in Maharashtra with granting licenses to vendors and traders.
- Gujarat is the only Indian state with a death penalty for the manufacture and sale of homemade liquor that results in fatalities. The legislation is titled the Bombay Prohibition (Gujarat Amendment) Act, 2009. The legislation was prompted by numerous deaths resulting from the consumption of methyl alcohol.
- Predictably, smuggling and illicit sale of alcohol are very common. “Folder” is a slang term of unknown origin, used in Gujarat to refer to a bootlegger who delivers alcohol on-demand.
Online Permits
- Foreigners and visitors from other parts of India can apply online for a permit. There are 35 stores across the state including nine in Ahmedabad that sell liquor on production of a physical copy of the permit. Once the permit expires, users are to hand-over the unconsumed liquor to the district collector.
Public Interest Litigation
- Five petitions, including Public Interest Litigation (PIL), have been filed before the Gujarat High Court challenging the prohibition law in the state. Most petitioners have raised concern that prohibition law violates Right to Privacy and are seeking relaxation on consumption in privacy.
Alcohol prohibition in Mizoram | UPSC – IAS
- The Mizoram Liquor Total Prohibition Act, 1995 banned sale and consumption of alcohol effective from 20 February 1997. In 2007, the MLTP Act was amended to allow wine to be made from guavas and grapes, but with restrictions on the alcohol content and the volume possessed. It is illegal to transport these products out of the state.
- Mizoram repealed prohibition on 10 July 2014, a period of 17 years after it had been imposed. On that date, the state Legislative Assembly passed the Mizoram Liquor (Prohibition and Control) Act, 2014 (MLPC Act), replacing the MLTP Act. The Presbyterian Church had organised mass prayers in all member churches across the state twice that year opposing the repeal of prohibition.
- The Mizoram Liquor (Prohibition and Control) Act, 2014 was repealed on 20 March 2019 with the Mizoram Liquor Prohibition Act, 2019, it was a legislation promised by the Mizo National Front. Rules are yet to be notified for the ban in the state.
Alcohol prohibition in Nagaland | UPSC- IAS
The Nagaland Liquor Total Prohibition Act, 1989 (NLTP Act) banned the sale and consumption of alcohol in 1989. Enforcement of the ban is lax and Indian Made Foreign Liquor is readily available. Authorities generally turn a blind eye towards illegal sales. Reports have stated that some police officials themselves engage in bootlegging. The Congress party has termed prohibition a “total failure” and has pleaded for it to be revoked.
- The excise department had earned around ₹600 lakh (equivalent to ₹47 crore or US$6.6 million in 2019) prior to prohibition.
- It earned about ₹10 lakh (US$14,000) annually in NLTP Act related fines as of June 2014. The Morung Express estimated that were about 500 illegal liquor bars in Dimapur, the largest city in the state, as of August 2014. Alcohol is also smuggled in from neighbouring Assam.
Alcohol prohibition in Lakshadweep | UPSC – IAS
Lakshadweep is the only union territory that bans the sale and consumption of alcohol. Consumption is permitted only on the island of Bangaram. Bangaram is an uninhabited island, but the Bangaram Island Resort has a bar.
States no longer practicing prohibition | UPSC – IAS
There are five States that no longer practicing prohibition. These states have previously enforced, but later repealed prohibition.
- Andhra Pradesh
- Haryana
- Kerala
- Manipur
- Tamil Nadu
Alcohol prohibition in Andhra Pradesh
- The total prohibition was introduced in Madras State (which included Coastal Andhra and Rayalaseema) when C. Rajagopalachari became Chief Minister in 1952. The ban was re-introduced by N. T. Rama Rao in 1994. N. Chandrababu Naidu repealed the prohibition in 1997, claiming that it was “not successful or feasible because of the leakages within the state and from across the borders”.
Alcohol prohibition in Haryana
- Bansi Lal led Haryana Vikas Party lift the prohibition on 1 April 1998. The total prohibition was in force in the state from July 1996.
Alcohol prohibition in Kerala
- Kerala currently allows alcohol to be served in most hotels, bars and airports. A ban imposed by the United Democratic Front government in 2014 was reversed by the Left Democratic Front government in 2017 when they came to power citing heavy losses in state revenue and sharp decrease in tourism industry.
- On 24 August 2014, Chief Minister Oommen Chandy announced that Kerala would implement prohibition in a phased manner. The decision was a result of factional conflict within the UDF, led by KPCC President V. M. Sudheeran. The decision was supported by the Catholic Church, Indian Union Muslim League (IUML) and the Kerala Congress. Liquor bars in Kerala are required to renew their licenses every year. The state government did not license any bars on 31 March 2014, resulting in the closure of 418 bars.
- The state government also declared its intention not to renew the licenses of the remaining 313 bars in the state. The state owned Kerala State Beverages Corporation (Bevco) had 338 shops, and Bevco would shut down 10% of them every year. Consumerfed, which has 46 shops, would also be closed. However, sale of alcohol would continue to be permitted in 5-star hotels, and there were fourteen 5-star hotels in the state as of August 2014. Toddy would also continue to be legally sold, and toddy shops would be permitted to operate as before. The state incurred heavy losses due to its tourism-based economy being severely affected by prohibition.
- However, after the 2016 Elections where the UDF was defeated by the LDF, the newly elected Chief Minister, Pinarayi Vijayan, reversed the policy of prohibition. The Chief Minister stated that the state’s policy would move from prohibition to regulation. In June 2017 the ban was revoked, allowing three stars hotels and above to openly serve alcohol to its customers.The restrictions on bars were also eased with bars being allowed to remain open till 2300 instead of previous 2200 with new bars being allowed to apply for license. Airport lounges were also allowed to start serving alcohol again.
Alcohol prohibition in Manipur
- Prohibition is enforced in the Imphal East, Imphal West, Thoubal and Bishnupur districts of Manipur. Prohibition was enforced statewide by the Raj Kumar Ranbir Singh government with effect from 1 April 1991. Local brews called ashaba and atingba are available in most areas, and authorities usually ignore their sale and consumption.
- In 2002, the Okram Ibobi Singh government lifted prohibition in the five hill districts of Manipur. The state Legislative Assemble passed the Manipur Liquor Prohibition (Amendment) Act, 2002 on 31 July 2002 lifting prohibition in the districts of Chandel, Churachandpur, Senapati, Tamenglong and Ukhrul.
In 2015, Chief Minister Okram Ibobi Singh stated in the Manipur state assembly that the state government was looking at the option of lifting prohibition in the state, but liquor ban still continues in the state.
Alcohol prohibition in Tamil Nadu
- The total prohibition was introduced in Madras State when C. Rajagopalachari became Chief Minister in 1952. In 1971, the DMK government led by M. Karunanidhi suspended it on 30 August 1971 and allowed the sale of arrack and toddy.
- In 1983, after previous serial introduction of prohibition and its revocation the state owned liquor distribution company TASMAC was established by the then Chief Minister M. G. Ramachandran. The TASMAC has a monopoly over wholesale and retail vending of alcoholic beverages. Since then, various prohibitions were installed in form of reduction of TASMAC shops, however, the alcohol selling is still legal.


