Table of Contents
The Impact of Extreme Weather on Inflation
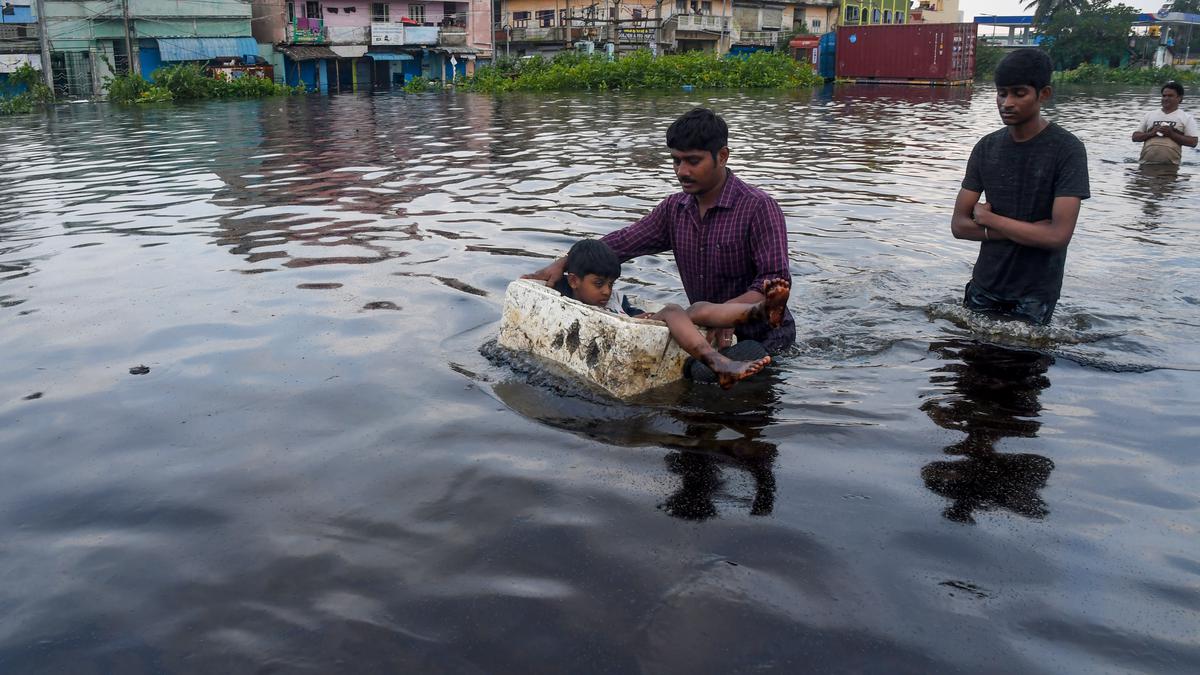

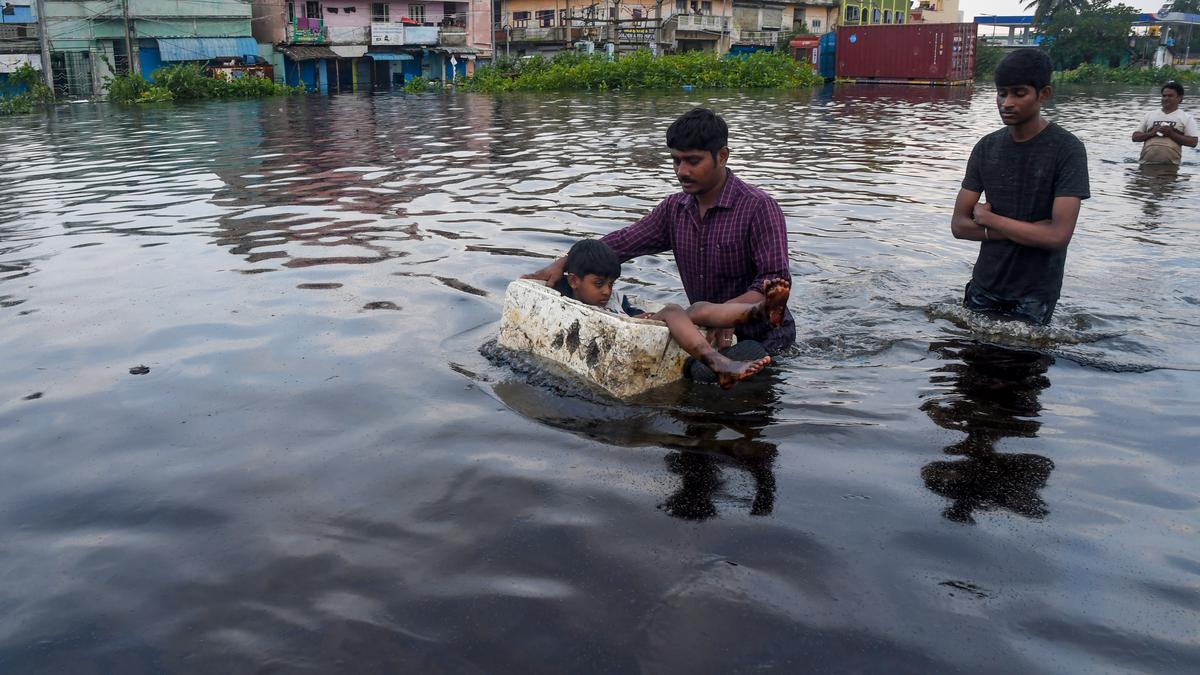
Extreme weather conditions may pose a risk to inflation, according to the Reserve Bank’s April Bulletin. This, along with prolonged geopolitical tensions that could keep crude oil prices volatile, is a growing concern for our economy.
Significance
The retail inflation, based on the Consumer Price Index (CPI), has eased to 4.9% in March after averaging 5.1% in the preceding two months. This can have a significant impact on monetary policy decisions and overall economic stability.
Features
- Extreme weather conditions
- Geopolitical tensions
- Volatility in crude oil prices
Objectives
The Reserve Bank mainly factors in CPI while arriving at its bi-monthly monetary policy decisions. The key interest rate has been kept unchanged at 6.5% since February 2023, citing concerns on the inflation front.
Effects
Global growth momentum has been sustained in the first quarter of 2024, and the outlook for world trade is turning positive. Treasury yields and mortgage rates are ticking up in major economies as expectations of interest rate cuts are being pared. In India, conditions are shaping up for an extension of a trend upshift in real GDP growth.
Pros and Cons
Pros: Strong investment demand, upbeat business and consumer sentiments, positive global growth momentum.
Cons: Potential risks of inflation due to extreme weather conditions, geopolitical tensions, and volatile crude oil prices.
Fun Fact
The views expressed in the Bulletin article are of the authors and do not represent the official views of the Reserve Bank of India.
Mutiple Choice Questions
1. What factor may pose a risk to inflation, according to the Reserve Bank’s April Bulletin?
a) Geopolitical tensions
b) Global growth momentum
c) Interest rate cuts
d) Consumer sentiment
Answer: a) Geopolitical tensions
Explanation: The Reserve Bank’s April Bulletin stated that extreme weather conditions and prolonged geopolitical tensions could pose a risk to inflation.
2. What was the retail inflation based on the Consumer Price Index (CPI) in March?
a) 4.9%
b) 5.1%
c) 6.5%
d) 4.5%
Answer: a) 4.9%
Explanation: The retail inflation based on the Consumer Price Index (CPI) was reported to be 4.9% in March.
3. What key interest rate has the Reserve Bank kept unchanged since February 2023?
a) 7.0%
b) 6.5%
c) 6.0%
d) 5.5%
Answer: b) 6.5%
Explanation: The Reserve Bank has kept the key interest rate unchanged at 6.5% since February 2023.
4. According to the article on ‘State of the Economy’ published in the Bulletin, what is turning positive?
a) Inflation
b) World trade
c) Interest rates
d) GDP growth
Answer: b) World trade
Explanation: The article on ‘State of the Economy’ mentioned that the outlook for world trade is turning positive.
5. What is the RBI’s stance on the views expressed in the Bulletin article?
a) They agree with all the views
b) They disagree with all the views
c) The views are of the authors and do not represent the RBI’s views
d) The views are endorsed by the RBI
Answer: c) The views are of the authors and do not represent the RBI’s views
Explanation: The RBI stated that the views expressed in the Bulletin article are of the authors and do not represent the views of the Reserve Bank of India.
Brief Summary | UPSC – IAS
The Reserve Bank of India’s April Bulletin highlighted that extreme weather conditions and geopolitical tensions could impact inflation. The retail based on the Consumer Price Index (CPI) eased to 4.9% in March. The RBI has kept the key interest rate unchanged at 6.5% since February. Global growth momentum has been sustained in the first quarter of 2024, and outlook for world trade is positive. India is expected to experience an increase in real GDP growth due to strong investment demand and positive business and consumer sentiments. The views in the article are of the authors and not the official position of the RBI.