Table of Contents
Kelp Forests and Climate Change | UPSC – IAS
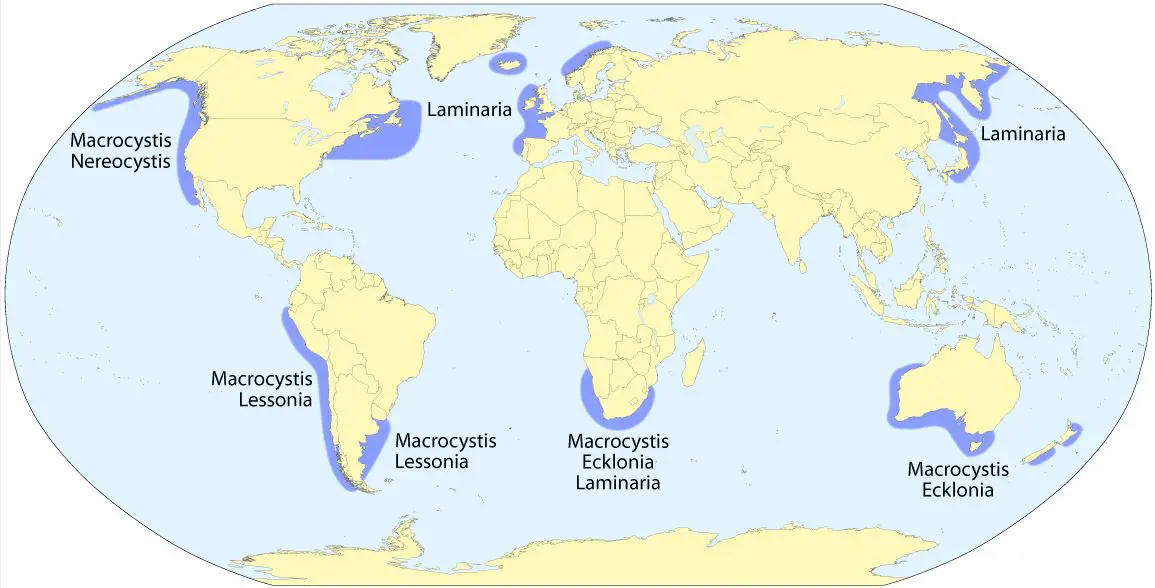
Kelp forests are underwater areas with a high density of kelp. They are recognized as one of the most productive and dynamic ecosystems on Earth. Smaller areas of anchored kelp are called kelp beds. Kelp forests occur worldwide throughout temperate and polar coastal oceans. They are large brown algae seaweeds. They grow in “underwater forests” in shallow oceans.
Generally speaking, kelps live further from the tropics than coral reefs, mangrove forests, and warm-water seagrass beds.
- Although kelp forests are unknown in tropical surface waters, a few species have been known to occur exclusively in tropical deep waters.
- Kelps and coral reefs are composed of algae that grow in the shallow parts of the ocean in warm and sunny waters.
- However, kelp forest grows in nutrient-rich waters while corals can develop in low nutrient waters.
The environmental factors necessary for kelp to survive include hard substrate (usually rock), high nutrients, clear shallow coastal waters and light.
- The productive kelp forests tend to be associated with areas of significant oceanographic upwelling.
- They are known for their high growth rate. Some varieties grow as fast as half a metre a day, ultimately reaching 30 to 80 metres.
Kelp Forest Deforestation | UPSC – IAS
Some of the drivers shifting kelp forests into degraded turf reefs are:-
- Marine heat waves,
- Strong storms,
- Expanding tropical herbivores,
- Gradual warming temperatures,
- Invasive species and nutrient pollution
Ocean warming and ocean acidification – can cause changes in the microbiome on the surface of Kelp, leading to disease symptoms like blistering, bleaching and eventually degradation of the kelp’s surface.
- The proportion of kelp showing signs of bite marks increased from less than 10% in 2002 to more than 70% in 2008, before there was no kelp to measure. At the same time the proportion of tropical fish in the ecosystem increased from less than 10% to more than 30%.
- This will affect the Kelp ability to photosynthesize and potentially survive.
- This could impact kelp forests around the world and potentially putting the marine biodiversity at risk, which thrives on these forests.
Significance of Kelp Forests | UPSC – IAS
- They are considered as Keystone Species and their removal is likely to result in a relatively significant shift in the composition of the community and perhaps in the physical structure of the environment.
- It provides as an important source of food for many marine species. In some cases, up to 60% of carbon found in coastal invertebrates is attributable to kelp productivity. It may be consumed directly or colonised by bacteria that in turn are preyed upon by consumers. Also, the rich fauna of mobile invertebrates in kelp beds makes this an important habitat in the diet of fish species. They provide a foraging habitat for birds due to the associated and diverse invertebrate and fish communities present.
- It increases productivity of the near shore ecosystem and dumps carbon into that ecosystem. Kelp primary production results in the production of new biomass, detrital material etc.
- It slows down the flow of the water which is important in situations where animals are spawning and releasing their larvae.
- They are natural breakwaters and prevent coastal erosion.
- They can influence coastal oceanographic patterns and provide many ecosystem services.
- It is an important source of potash and iodine. Many kelps produce algin, a complex carbohydrate useful in industries such as tire manufacturing, ice-cream industry.
Kelp Forest Salinity | UPSC – IAS
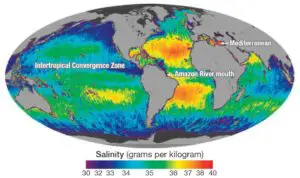
- Kelp forests are found in cold, nutrient-rich water and are found in the shallow coast. Kelp forests have a very high salinity.
- They are usually in a water temperature in the 50-65 degree range.
- Kelp forests are not deeper than 80 feet and almost never shallower than 20 feet.
- The kelp life can be shorter if winter is longer
- These brown algae communities live in clear water conditions through which light penetrates easily.